A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Hardware Components
Computers have become an integral part of our daily lives. Statistics show that we have some type of electronic device with us most of the time. A study published in 2021 shows that 92% of American households have at least one type of computer. Whether for work, education, or entertainment, 85% of Americans go online every day. Additionally, this recent report shows that the average American spends over 7 hours in front of a screen daily. With so much of our lives connected to electronic devices, having a solid understanding of computer or device specifications will help you understand what’s happening with your device. It can also help you make educated decisions when it comes time to purchase or upgrade the device.
Computer Components:
So, what does device specifications even mean? We’re glad you asked! It refers to the hardware components that make up a computer or mobile device. You’ll see or hear them when you search for a laptop or mobile device, and they generally have numbers associated with them. These specifications determine your device’s performance, capabilities, and suitability for various tasks. Some of the key components of a computer include central processing unit (CPU), random-access memory (RAM), storage devices, and operating system.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU, often referred to as the brain of the computer, is arguably the most crucial component in a computer system. Simply put, it’s a set of circuits that run the machine’s operating system and apps. It’s responsible for interpreting, processing, and executing instructions and performing calculations that drive all tasks and processes. Without the CPU, your device simply won’t work. The main things to watch when checking out your CPU are architecture and number of cores.
Architecture:
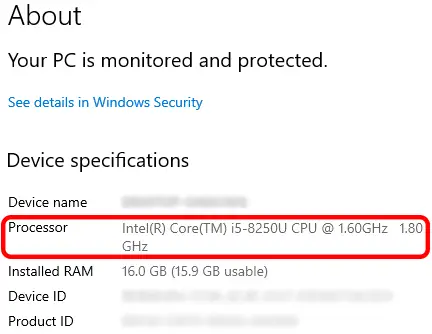
The CPU’s architecture determines its efficiency and performance. Currently, the most commonly used architecture in computers is x86-64. This type of architecture is produced by either Intel or AMD and incorporate advanced technologies that allow you to complete tasks efficiently. Processers are produced in series and generations. For example Intel has an i-series processor that has been made over multiple years. The higher the series (ex. i5, i7, i9 etc.) the more efficient the device can run. As time progresses, the producer of the processer finds ways to make it work more efficiently. This means that a newer generation of a particular series will run smoother than an older one. For example, an i7 gen 1 will be slower than an i7gen 12. You can find out which processor your device has by going to the about tab on your computer.
Number of Cores:
The number of cores represents the number of individual processing units within the CPU. In the early days of computers, CPUs had a single core and could complete one task at a time. Today’s CPUs can have multiple cores that allow the CPU to handle multiple tasks simultaneously and improe overall performance. Dual-core CPUs have two cores, quad-core CPUs have four cores, and so on. While it is common for PCs to use multiple identical cores, some of the newer multi-core CPU’s have what are called efficiency cores. If all cores are identical, this means that all the processors are high performance and optimized the same way. If your device has efficiency cores, some will be reserved for background and low demand tasks and others will be utilized for high performance tasks
Computer Memory and Storage
When it comes to computers, we want our devices to work quickly and be able to store a lot of information. The reason is because as technology progresses, the applications we use on those devices require more and more resources to work efficiently. As an example, Windows 10 operating system takes about 16G of space, while Windows 11 operating system takes roughly 27G. This is where RAM and storage come in. Storage refers to the amount of information your device can save. Ram refers to how quickly your device can retrieve that information so the CPU can process it.
Storage Devices
Storage devices are essential for saving data and files permanently. When looking at the specs of a computer or laptop, this number will be the highest number you see and is typically measured in either GB or T. There are two primary types of storage devices: Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs).
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs):
Hard Disk Drives were introduced by IBM in 1956 and were initially used as a secondary storage device. The original ones could store a whopping 3.75M of data! Today they can be used as an internal or external drive to save data you need to access and come with a lot more storage capacity. HDDs store data on spinning magnetic platters and use read/write heads to access data. They offer large storage capacities and are commonly used in budget-friendly laptops or in situations that require bulk storage such as a camera system NVR. As time goes on, HDD users may start to experience a hard disk drive lagging, slow start ups or longer load times. If this happens, replacing the drive can help prolong the life of your device.
Solid State Drives (SSDs):
Solid State Drives are a new generation of storage used in computers. SSDs use flash memory to store data, offering significantly faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs. Unlike HDDs, solid state drives have no moving parts. The data is written, transferred, and erased electronically and silently. They enhance system responsiveness, reduce boot times, and improve overall performance. Although typically more expensive than HDDs, SSDs have become increasingly popular for their speed and reliability.
Random-Access Memory (RAM)
RAM is the temporary working memory of a computer. This is generally the smaller number on your computer specs when you are reviewing them. RAM is the messenger between your storage drive and CPU and allows for quick access to data. It will temporarily store data and instructions while it is actively running programs. When you are done with that project, it will store the information on the storage drive and make room for other information. The amount of RAM in your device can significantly impact multitasking and overall system performance.
Capacity:
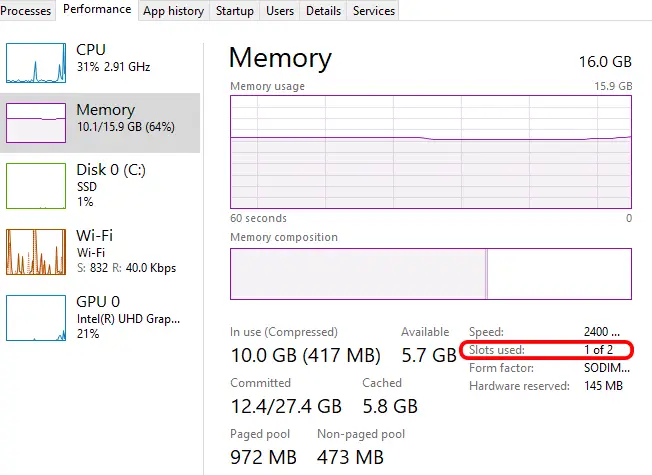
RAM capacity is measured in gigabytes (GB) and determines how much data the computer can hold in its working memory. They come in 1G and can go up to 128G or higher. PCs can have multiple slots to hold random access memory on the motherboard and you can put memory in 1 or more of the slots. More RAM allows the computer to handle complex tasks and run multiple applications smoothly. Just remember that you if you have more than 1 slot, you want to make sure that the RAM in both slots matches. Otherwise, the computer will adjust the speeds to reflect the slowest one you have plugged in. For example, if you have a 4 GB RAM in one slot and a 16 GB RAM in another, the computer will recognize 8 GB (4 GB on one and 4 GB on the other) instead of the combined 20 GB.
To find out how many slots your computer has, you can view the memory section of your task manager.
Type:
When searching for RAM, you should be aware that there are various types of RAM exist, such as DDR (Double Data Rate), DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4. Newer generations offer improved speed and efficiency. Not all RAM is the same or compatible with all devices. Before picking which RAM you want, double check that it is compatible with the motherboard in your machine. Other things you should note is that DDR and PC are interchangeable prefixes, but if the specs have an L at the end, that means the RAM operates at a lower voltage and will need to be matched. Laptop RAM is classified in the same way, but is smaller than workstation RAM and will not work unless plugged into a laptop.
Operating system
An operating system is the software that supports a computer’s basic functions and manages all of the other applications you load. All electronic devices come preloaded with an operating system or OS that runs programs, stores files, connects to networks and countless other things that would be burdensome to do manually. The operating system works with your hardware to provide you a device that can accomplish great things.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows comes preloaded on most computers. Windows devices used in a business setting, should be purchased with the professional version of the operating system that’s available. For example Windows 10 pro or Windows 11 pro. The professional version of an operating system provides benefits like drive encryption, group policy controls, remote desktop, and other commonly used business features. Since it is more expensive to upgrade computer that is loaded with home edition to the professional edition than it is to just purchase the professional edition out right, it’s best to start off on the right track with the professional edition of your OS.
Mac OS
This OS runs apple computers and laptops. Unlike Microsoft Windows, there is not a professional version of Mac OS. As long as you have the most recent update of the OS, you will have all of the security and operational features that the OS provides.
Need more help with your work computers?
If your business needs help managing your devices, let us know. IT Enabled is a managed IT service provider. We help organizations with 5-500 employees tackle technology issues by providing comprehensive IT including network and tech support, such as computer, laptop and server support, cybersecurity, disaster recovery options and business phone systems. Our business is keeping you focused on your business.
Want to read more?
Check out our other blogs including How to speed up your device.
